
IT Guides and CyberSecurity News
Security News
Android apple APT Breach chrome cloud Crypto miner CryptoStealer cyberattack Cybersecurity Email EMotet Facebook Firewall google ads GooglePlay Guide infostealer Linux Malicious malicious Ads Malware MS365 Network Segmentation NGFW Phishing Phising POWERSHELL PyPL python Ransomware RAT security stealer Tips trojan VM VPN vulnerability Vulnerability Assessment Windows Windows 10 windows 11 Windows Server wordpress
- 6 HIDDEN THREATS IN CORPORATE EMAIL
 The best place to hide a book is in a library. The most ideal place to hide a leaf is in the forest. And the best way to hide a suspicious email? In plain sight. Email security fraud is now so common that most internet users are now aware of basic hacker tricks, such as… Read more: 6 HIDDEN THREATS IN CORPORATE EMAIL
The best place to hide a book is in a library. The most ideal place to hide a leaf is in the forest. And the best way to hide a suspicious email? In plain sight. Email security fraud is now so common that most internet users are now aware of basic hacker tricks, such as… Read more: 6 HIDDEN THREATS IN CORPORATE EMAIL - EMAIL ACCOUNT TAKEOVER:BEST PRACTICES FOR REDUCING RISK
 How account takeovers work Account takeover – the criminal use of compromised online accounts – has the potential to be immensely profitable. Hackers steal credentials from individuals (see phishing) or target an entire organization using bots. They then use these stolen credentials to take ownership of the compromised accounts or sell credentials lists to other cybercriminals. Whoever… Read more: EMAIL ACCOUNT TAKEOVER:BEST PRACTICES FOR REDUCING RISK
How account takeovers work Account takeover – the criminal use of compromised online accounts – has the potential to be immensely profitable. Hackers steal credentials from individuals (see phishing) or target an entire organization using bots. They then use these stolen credentials to take ownership of the compromised accounts or sell credentials lists to other cybercriminals. Whoever… Read more: EMAIL ACCOUNT TAKEOVER:BEST PRACTICES FOR REDUCING RISK - Big Head Ransomware
 TrendMicro analyze the technical details of a new ransomware family named Big Head. Big Head, which came out in May 2023, has at least three variants, all designed to encrypt files on victims’ machines to extort money, like other ransomware variants. One Big Head ransomware variant displays a fake Windows Update, potentially indicating that the… Read more: Big Head Ransomware
TrendMicro analyze the technical details of a new ransomware family named Big Head. Big Head, which came out in May 2023, has at least three variants, all designed to encrypt files on victims’ machines to extort money, like other ransomware variants. One Big Head ransomware variant displays a fake Windows Update, potentially indicating that the… Read more: Big Head Ransomware - MoveIT vulnerability exploited by Ransomware Gang
 The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) and the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) are releasing this joint CSA to disseminate known CL0P ransomware IOCs and TTPs identified through FBI investigations as recently as June 2023. According to open source information, beginning on May 27, 2023, CL0P Ransomware Gang, also known as TA505, began exploiting… Read more: MoveIT vulnerability exploited by Ransomware Gang
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) and the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) are releasing this joint CSA to disseminate known CL0P ransomware IOCs and TTPs identified through FBI investigations as recently as June 2023. According to open source information, beginning on May 27, 2023, CL0P Ransomware Gang, also known as TA505, began exploiting… Read more: MoveIT vulnerability exploited by Ransomware Gang - Info Stealer named Skuld
 In May 2023, the Trellix Advanced Research Center discovered a new Golang stealer, known as Skuld, that compromised systems worldwide. The malware targets sensitive information stored in certain applications, such as Discord and web browsers, and the Windows system. The author, Deathined, has taken inspiration from different open-source projects and malware samples to build up… Read more: Info Stealer named Skuld
In May 2023, the Trellix Advanced Research Center discovered a new Golang stealer, known as Skuld, that compromised systems worldwide. The malware targets sensitive information stored in certain applications, such as Discord and web browsers, and the Windows system. The author, Deathined, has taken inspiration from different open-source projects and malware samples to build up… Read more: Info Stealer named Skuld - Satacom Downloader Delivers Cryptocurrency Stealer
 Satacom downloader, also known as LegionLoader, is a renowned malware family that emerged in 2019. It is known to use the technique of querying DNS servers to obtain the base64-encoded URL in order to receive the next stage of another malware family currently distributed by Satacom. The Satacom malware is delivered via third-party websites. Some… Read more: Satacom Downloader Delivers Cryptocurrency Stealer
Satacom downloader, also known as LegionLoader, is a renowned malware family that emerged in 2019. It is known to use the technique of querying DNS servers to obtain the base64-encoded URL in order to receive the next stage of another malware family currently distributed by Satacom. The Satacom malware is delivered via third-party websites. Some… Read more: Satacom Downloader Delivers Cryptocurrency Stealer - Commercial Spyware on the Rise
 Commercial spyware use is on the rise, with actors leveraging these sophisticated tools to conduct surveillance operations against a growing number of targets. Cisco Talos’ research specifically looks at two components of this mobile spyware suite known as “ALIEN” and “PREDATOR,” which compose the backbone of the spyware implant. PREDATOR is an interesting piece of… Read more: Commercial Spyware on the Rise
Commercial spyware use is on the rise, with actors leveraging these sophisticated tools to conduct surveillance operations against a growing number of targets. Cisco Talos’ research specifically looks at two components of this mobile spyware suite known as “ALIEN” and “PREDATOR,” which compose the backbone of the spyware implant. PREDATOR is an interesting piece of… Read more: Commercial Spyware on the Rise - Harbot Banking Trojan Targets Americas
 Cisco Talos has observed a threat actor deploying a previously unidentified botnet program Talos is calling “Horabot,” which delivers a known banking trojan and spam tool onto victim machines in a campaign that has been ongoing since at least November 2020. The threat actor appears to be targeting Spanish-speaking users in the Americas and, based… Read more: Harbot Banking Trojan Targets Americas
Cisco Talos has observed a threat actor deploying a previously unidentified botnet program Talos is calling “Horabot,” which delivers a known banking trojan and spam tool onto victim machines in a campaign that has been ongoing since at least November 2020. The threat actor appears to be targeting Spanish-speaking users in the Americas and, based… Read more: Harbot Banking Trojan Targets Americas - Amadey’s Multi-Stage Attack Malware Explained
 McAfee Labs have identified an increase in Wextract.exe samples, that drop a malware payload at multiple stages. Wextract.exe is a Windows executable file that is used to extract files from a cabinet (.cab) file. Cabinet files are compressed archives that are used to package and distribute software, drivers, and other files. It is a legitimate… Read more: Amadey’s Multi-Stage Attack Malware Explained
McAfee Labs have identified an increase in Wextract.exe samples, that drop a malware payload at multiple stages. Wextract.exe is a Windows executable file that is used to extract files from a cabinet (.cab) file. Cabinet files are compressed archives that are used to package and distribute software, drivers, and other files. It is a legitimate… Read more: Amadey’s Multi-Stage Attack Malware Explained
IT Guides
-
6 HIDDEN THREATS IN CORPORATE EMAIL
The best place to hide a book is in a library. The most ideal place to hide a leaf is in the forest. And the best way to hide a suspicious email? In plain sight. Email security fraud is now so common that most internet users are now aware of basic hacker tricks, such as frequent misspellings and suspicious links. Yet even so, phishing emails are a top point of entry for ransomware, making up 54 percent of digital vulnerabilities in 2020.
But what about the email security threats that aren’t as common? These types of threats can be even more successful because they aren’t as well known.
Here are six hidden threats of corporate email, some of which you may have heard or thought of and others perhaps you haven’t.
1.Unintentional acts by authorized users – Email security threats aren’t always intentional. Sometimes, they come from well-meaning corporate employees who simply make a mistake. Authorized users may accidentally send sensitive information via email to someone they trust (or who is acting as someone they trust), potentially exposing the organization to risk and potential brand reputation. That’s why it’s so important to train users on what types of information should and should not be shared through specific channels like email.
2.Improper Management Controls – Having properly defined management security controls is crucial for any organization. These controls could include company-wide security policies and processes, change control and configuration management, scheduled risk assessments, and contingency planning, and recurring annual or twice annual training for all employees, among other safeguards. Without these safeguards, employees are at risk of social engineering attacks like phishing, whaling, or ransomware.
3.Ransomware – Ransomware email messages contain or point to a common hacker tool: malware. This particular type of malware is designed to encrypt files and documents. Once they are encrypted, ransomware attackers contact the affected individual and demand payment for recovery for their locked information. Ransomware may be less common than other social engineering attacks, but it can have hefty consequences. It is never advisable to pay for ransomware. Instead, work with law enforcement and cybersecurity experts.
4.Authentication Attacks – Sometimes, a hacker’s target is the email inbox itself. During authentication attacks, hackers attempt to break an email server’s authentication and gain access directly to email messages and attachments stored in that server. They then have access to do with that information what they will. That’s why it’s important to ensure your authentication methods are rock-solid.
5.Whaling – You’ve probably heard about phishing, a type of social engineering in which hackers pretend to be from reputable companies so that they can encourage unsuspecting victims to give up personal or sensitive corporate information. But have you heard of “whaling?” While hackers may not be choosy about who they target, scammers who ”whale” set their sights higher, targeting high-level executives in corporate organizations. And, they do their research. Whaling often relies on publicly-available information like that available on social media profiles to build credibility with the target. See our recent blog for more details on how to combat this common threat.
6.DDoS and Bot Attacks – Email security can be a warzone. With malicious bot and DDoS attacks, hackers can use hijacked botnets to send huge amounts of emails to an organization with the goal of crashing the email server due to system overload. Typically, web servers come under attack for B2C (business-to-customer) organizations that generate eCommerce sales, whereas email server attacks are commonly run on email servers, as this is where sensitive corporate information regarding sales and other information changes hands. This is where spam filtering becomes increasingly important.
-
EMAIL ACCOUNT TAKEOVER:BEST PRACTICES FOR REDUCING RISK
How account takeovers work
Account takeover – the criminal use of compromised online accounts – has the potential to be immensely profitable. Hackers steal credentials from individuals (see phishing) or target an entire organization using bots. They then use these stolen credentials to take ownership of the compromised accounts or sell credentials lists to other cybercriminals.
Whoever uses the list can then impersonate users to steal funds or data, install malware or ransomware, or simply cause havoc through malicious acts. This can often happen within hours of the data breach taking place.
In May 2022, the FBI issued an alert that they had “observed incidents of stolen higher education credential information posted on publicly accessible online forums or listed for sale on criminal marketplaces”. Originally, botnets were used to deliver massive volumes of spam, and responsible for 90% of the malware spread by email worldwide. Most of the biggest spam-sending botnets have been taken down, with Necrus botnet being the last, defeated by Microsoft in 2020.
Since then, botnets have evolved, and are now being used to dispatch credentials to gain control of legitimate accounts, leading to a rapid escalation in the number and value of ATO attacks taking place each year.
Every organization is at risk
As well as opening the door to fraudulent financial transactions, it can enable cybercriminals to conduct more phishing attacks on more target individuals, departments, and organizations – not just ecommerce and financial businesses, but also healthcare, government agencies, and academic institutions.
Email can be particularly vulnerable to ATO
Impostors know that sending a fraudulent email from a legitimate email account means that traditional anti-phishing software is unlikely to flag their activity as suspicious, and recipients are more likely to trust the sender and to do what they ask.
Once cybercriminals have gained access to an account, they can change anything related to its use, such as security questions, passwords, and encryption settings. This complete takeover makes it impossible for the real owner to gain access and can even cast suspicion on them or cause reputational damage.
Account takeover protection and prevention
The speed and evolution of today’s attacks present significant challenges for all organizations. Unfortunately, some of the most commonly used techniques aren’t enough to stop ATO, but there are some best practices that you should follow to help reduce risk.
- Adopt a strong password policy
Many accounts are easy to crack because of old, weak, or repeated passwords. Use a password manager with strong passwords. - Check for compromised credentials
Regularly check the credentials of new users against a breached credentials database. - Limit the number of login attempts
Locking an account after a set number of login attempts, based on username, device, and IP address, can help prevent account takeover. - Set multi-factor authentication
Use a multi-factor authentication (MFA) method, such as tokens, biometrics, SMS access code or mobile app. - Notify users of account changes
Send your users a notification of any changes to their account, so they can quickly spot if their account has been compromised and altered by someone else.
Introducing the Libraesva Adaptive Trust Engine
People’s level of trust tends to be based on experience, building over time as meaningful interactions take place. Using a similar experience-based approach, Libraesva’s Adaptive Trust Engine uses AI and machine learning to recognize the usual communication patterns of your email users and recipients. It dynamically tracks and monitors transactions to measure trust and behaviors, and uses history to understand what’s normal activity for each account.
The Adaptive Trust Engine is part of Libraesva’s Email Security Gateway solution. It swiftly spots deviations and anomalies to stop first-time senders from delivering malware to accounts within your organization. It also works on outgoing traffic, preventing impostors from sending out spam from a compromised mailbox. From a user perspective, it’s unobtrusive – running in the background and only sending alerts when needed.
- Adopt a strong password policy
-
Tips And Best Practices For Small Business Email Management
One of my friends, Janet, is a classic example of why you need email management in your business. She constantly receives hundreds of emails at work. One day, she had an important client presentation in the afternoon. But the client sent her an email the previous night rescheduling the meeting to the early morning instead. By the time she got to work, she should’ve already started with her presentation.
Unfortunately, her inbox was already full of office news messages and newsletters. So by the time she sorted through them and found the client’s email, it was already too late. Her company ended up losing a valuable client contract. She wouldn’t have been stuck in this situation if she had applied email management best practices.
Janet’s situation might sound all too familiar. Perhaps you’ve had a similar blunder or watched a similar situation unfold with one of your employees. Either way, it’s damaging to your business. To help you avert this crisis in the future, I’ll take you through what email management is and how it can help your business. Lots of things to go over, so let’s get started, shall we?
-
Manually Creating Swap Partition
Continuing from this articles…https://anyware.com.sg/re-sizing-linux-storage/
What happened to Swap….
Creating Swap partition alone would not suffice that it would be used by the system; it has to be initialized and activated.
To initialize:
# mkswap /dev/sda5
To activate:
# swapon /dev/sda5
When I recreated the partition I didn’t know about the above and this…
New Swap partition’s UUID had to update in /etc/fstab
How to get the UUID, run this command:
# blkid | grep swap | awk '{print $2}'Echo out the UUID into /etc/fstab file and use the same as the previous swap entry

Mount the swap with this command:
# mount -a
Well that fixed the missing swap issue….
The final issue to address ” Gave up waiting for suspend/resume device” message at boot time
Don’t take me as a genius here… the fixes for the issues are all obtained by googling…credit goes to the original solution posters.
The solution given was to remove
/etc/initramfs-tools.conf.d/resume
and then run
update-initramfs -u
Well… did the above but the system went into a hung state with heavy CPU usage after reboot.
As I always do in such cases, force restart the system into safe mode and then rebooted in to normal state…. Viola… no issue or Errors.
-
Re-Sizing Linux Storage
Continuing from this article https://anyware.com.sg/debian11-128mb/
While testing out the file server services; the storage space soon filled up.
That’s when I realised I had provisioned only 16GB of Storage most likely I thought I’m won’t doing anything else besides sftp testing.
So how exactly I increased the Storage size…
There are couple of options in hand for me to do this.
- Add Additional virtual disk and mount it as a folder for the shares
- Expand the current virtual disk and partition the extra free space and mount it as a shared folder
- Expand the current virtual disk and repartition the disk so there is no need for additional mounts
Since I was in experimenting mood, I opted for option 3.
The process would like this or at least I thought so:
- Expand virtual disk to 120GB
- Delete the current partition and recreate it
- Resize the volume to take up the full capacity of the disk.
The actual process as I had to do additional procedures to correct some of the actions which didn’t go as expected:
- Expand virtual disk to 120 GB – > easy peasy..
- Delete the current partition and recreate it
I wasn’t so sure if this would go well but who cares its my test system anyway…
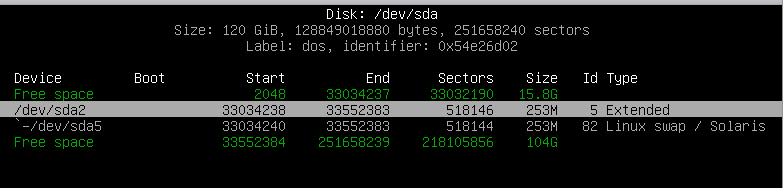
I used
cfdisk
which is more user friendly.
Deleted the primary, extended and linux swap partitions
Then readded the partitions with larger Primary partition with 116GB space, next extended and swap partition.
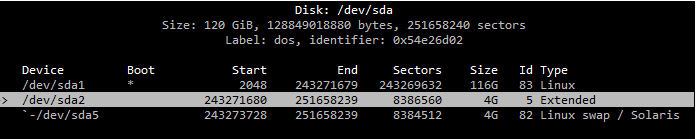
Paid particular attention to enable Boot on primary partition, before committing the changes.
So far so good…. ran
resize2fs /dev/sda1
hoping to see the new disk size.
The command returned to say something like .. no changes found no changes made.
Thought rebooting the system would show the increase in partition orrr break the system….
The reboot happened but it took way longer to then usual. There were error messsages like “missing swap partition” and “Gave up waiting for suspend/resume device”
Didn’t knew what it meant so proceeded to resize the volume and this time the volume expansion was successful and it showed the full volume size
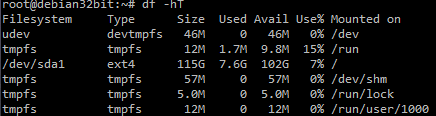
Then checked up why swap was not in use… that’s when I found that couple on things must be done to fix it.
What happened to Swap….
Creating Swap partition alone would not suffice that it would be used by the system; it has to be initialized and activated. Please read to this linked article on how to activate swap partition
-
Debian 11 on 128 MB RAM
Coming from Win 3.1 days, I can’t fathom what the craze with modern operating systems gobbling GBs of RAM. Therefore I took it on myself to find which modern OS can smoothly run with the least amount of RAM. So I set out some parameter the OS should server, like it should have the complete networking stack with the latest security modules like network encryption and system utilities.
The OS : Debian 11, the latest release, and the least RAM the installer allows is 128 MB.
Function of the system: Secure File Transfer ServerRead on the see the challenges I encountered with Text Mode setup and the arcane file partitioning process
The Process
I started the VM with 64MB ram; the installer aborts with insufficient RAM message
And I doubled the size to 128MB, this time the installer came up with a different message: Warning message of Low ram and the minimum of 273 ram required to successfully complete the installation. It didn’t stop me from proceeding next…
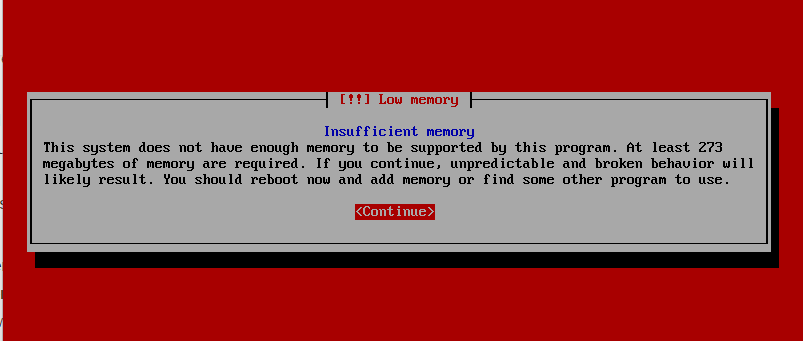
Low Memory install mode.
In this mode, the installer doesn’t load up all drivers/modules which would cater to larger hardware types; instead it prompts for hardware type to load.
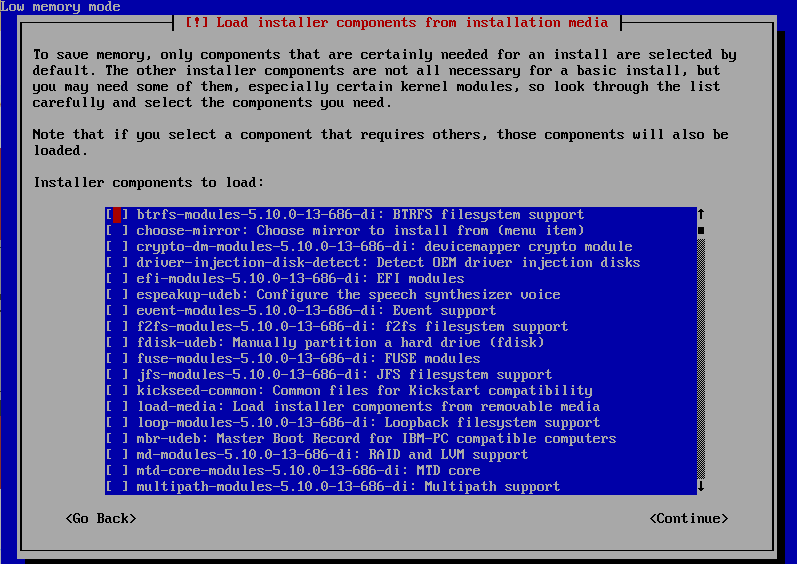
I selected the following modules from the above options for my vm type:
- Choose mirror
- NIC modules
- MBR
- Parted
- Partman -Auto
When prompted for NIC selection, its impossible to go to the next with wrong NIC type. The installer verifies the selection first just like the good old days of installing linux/windows 95.
Low RAM didn’t have much impact on the installation process, it completed only about couple of seconds slower than a VM with about 2GB RAM.
Performance
Minute boot delay compared to standard with 2GB of RAM.
It handled multiple sftp connections without dips in the transfer chart
Tried both SFTP and SMB services, the os can manage these services pretty well.
Transferring files via SMB files peak up to 800Mbs.
So what a VM of 128MB gives you…
- File server catering to up 10 users
- SSH based vpn
- SFTP server
- Open VPN server
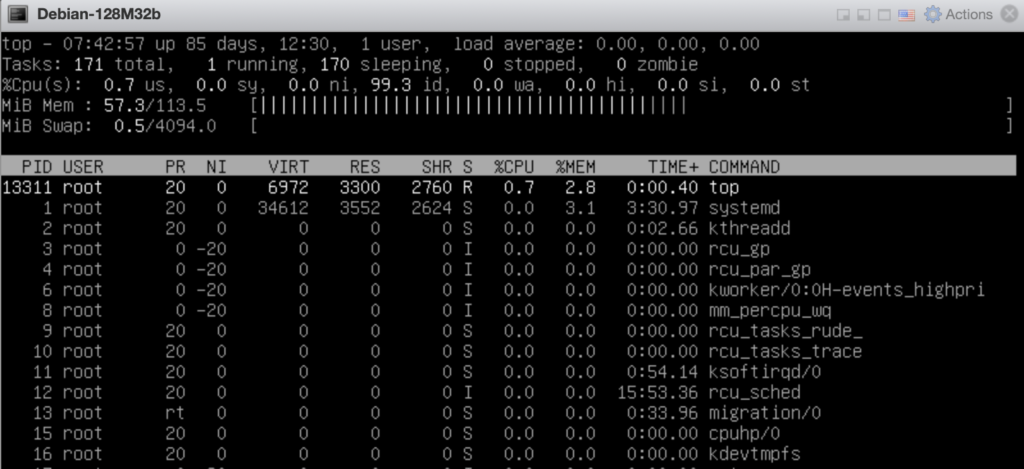
memory utilisation There you have, Debian 11 32bit running on 128 MB RAM and utilising half the resource while running idle.
-
Phishing Activities in 2022
Phishing scams continue to plague the internet in 2022, more now than ever. This article explores the latest data and current trends and shows you how to avoid a phishing attack today.
Cybercrime consultants have found over a million discrete phishing attacks perpetrated this year, which is up by 61% in the same time period in 2021.
In a recent sophisticated phishing attack, customers of the Dutch bank MKB were targeted with a fake newsletter that purported to be from MKB.
The newsletter asked customers to follow a link to find out more about how the bank was supporting customers through the pandemic. The link took victims to a phony authorization page that stole their Outlook login credentials.
This is the kind of cybercrime that was on the rise in 2022.
More news/attack information unfolds in the complete article in the link below:
https://www.wizcase.com/blog/phishing-wrapping-up-a-record-breaking-year/
-
What is Advanced Malware Protection
Malware is a serious threat to both individuals and enterprises. It can compromise your sensitive data, disrupt operations, and even cause physical damage to computer systems. That’s not the end of the rope, though. If malware infects your system, it could severely damage your company’s reputation in the case of a data breach. In addition, data breaches usually require a settlement to affected customers, which is very costly. As if regular malware wasn’t enough, we’ve got bigger, smarter, and worse malware out there. So, it’s important to have advanced malware protection in place to protect your enterprise.
In this article, We’ll see what is advanced malware protection and its importance for your business. You’ll also gain a complete understanding of its 4 different types. So without further ado, let’s find out what advanced malware is.
Read more :
-
How to beef up Microsoft 365 Security
Microsoft has long used a shared responsibility model for its various cloud services, including Microsoft 365. The model states that Microsoft is responsible only for securing its cloud infrastructure. This means users are responsible for securing their data. But the problem is Microsoft 365 isn’t secure by default. So how do you get around this issue and improve Microsoft 365 security?
Microsoft 365 deployments have several built-in security mechanisms. You’ll need to take advantage of these mechanisms to get around this issue. Although many security settings are available, some are more important than others. In this article, I’ll discuss 4 key areas to focus your efforts on if you’re just starting with Microsoft 365 security
Tech News
-

Windows Server updates has Bugs
Read more: Windows Server updates has BugsHere’s a recently identified problem we’ve been following that can impact your Active Directory environment: New Windows Server updates cause domain controller freezes, restarts (Bleeping Computer) Windows Server November 2022 updates cause LSASS memory leak (Günter Born)
-

Windows Tech Tips and Tricks
Read more: Windows Tech Tips and TricksHow to Remove Windows 10’s Annoying Search Highlights Icons (Tom’s Hardware) How to auto shutdown Windows when it’s been idle for a while (OnMSFT) How to Transfer a Windows 10 or 11 License to Another PC (Tom’s Hardware) How to Run a Program as a Different User (RunAs) in Windows? (Windows OS Hub) How to Keep Windows Running Smoothly (Tom’s…
-

Linux Tech Tips
Read more: Linux Tech TipsUbuntu Tips How to Install Ubuntu 22.04 Desktop [Step by Step Picture Guide] (Ubuntu Handbook) How to Upgrade to Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Using ‘do-release-upgrade’ Command (Allthings.how) How to enable SSH 2FA on Ubuntu Server 22.04 (TechRepublic) Install Grub Customizer to Configure the Boot Menu in Ubuntu 22.04 (Ubuntu Handbook) 31 Linux Commands Every Ubuntu User…
-

Removing Uninstalled Software Data from Windows
Read more: Removing Uninstalled Software Data from WindowsIt’s common for Windows users to uninstall applications from their computers. It’s pointless to keep applications on your disk if you no longer use them. Unfortunately, when you uninstall an application, some of its data may remain on the hard disk. To make matters worse, these application remnants sometimes contain sensitive data. In this article,…
-

Microsoft 365 Tips and Tricks
Read more: Microsoft 365 Tips and TricksUnderstanding Microsoft 365 security for your environment Why MFA Is More Important than Ever for Microsoft 365 How To Adjust The Multi-Factor Authentification (MFA) For Microsoft 365 How to Build Workflows Using Power Automate and AI in Microsoft 365 Microsoft 365 Login: Troubleshooting User Sign-In Problems How to Prevent Microsoft 365 From Purging Old Messages…
-

Windows Tech News
Read more: Windows Tech NewsWindows 11 22H2 no longer supports Software Restriction Policies (SRP) (Günter Born) Microsoft WinGet package manager failing due to CDN issues (Bleeping Computer) Turns out shutting off Windows 11 security features helps Intel graphics cards performance, too (OnMSFT) Windows Server news Microsoft: Server Manager disk resets can lead to data loss (Bleeping Computer)
Android apple APT Breach chrome cloud Crypto miner CryptoStealer cyberattack Cybersecurity Email EMotet Facebook Firewall google ads GooglePlay Guide infostealer Linux Malicious malicious Ads Malware MS365 Network Segmentation NGFW Phishing Phising POWERSHELL PyPL python Ransomware RAT security stealer Tips trojan VM VPN vulnerability Vulnerability Assessment Windows Windows 10 windows 11 Windows Server wordpress
